HI-Quik Procalcitonin (PCT) Rapid Card Test
Assisting Timely Diagnosis of Sepsis, Saving Lives
- Sensitivity of 1 ng/ml helps tracking of sepsis at very early stage
- Sample Types: Whole Blood, Serum, Plasma
- Whole Blood Protocol -True Point-of-care Test for Hospitals and Nursing homes
- Fast testing time of 15 minutes, immediate medical treatment
- 2-30 O C Storage suitable for all type of environment
- Convenient Pack-size of 5 Test suitable for all workloads
HI-Quik Procalcitonin Rapid Test can be used as initial Screening test for high risk group. A positive result indicates Sepsis risk and then the patient can be further checked for Quantitative Values of Procalcitonin at regular intervals to monitor the levels.
ICU
Organ Transplant
Diabetic
Low immunity
Sepsis:
Sepsis is the result of a massive immune response to bacterial infection that gets into the blood. It often leads to organ failure or injury, and the critical condition often leads to death.
Sepsis
- Fever above 101 degree or a temperature below 96.8 degree
- Heart rate higher than 90 beats per minute
- Breathing rate higher than 20 breaths per minute
- Probable or confirmed infection
Severe Sepsis:
- Organ failure
- Patches of discoloured skin
- Decreased urination
- Changes in mental ability
- Low platelet (blood clotting cells) count
- Problems breathing
- Abnormal heart functions
- Chills due to fall in body temperature
- Unconsciousness
- Extreme weakness
Septic shock
- Symptoms of severe sepsis PLUS a very low blood pressure
- Young children and seniors
- People with weaker immune systems, such as those with HIV or those in chemotherapy treatment for cancer, Diabetics
- People being treated in an intensive care unit (ICU) for surgeries, organ transplant
- People exposed to invasive devices, such as intravenous catheters or breathing tubes
- 1 in 4 patients in ICU suffer sepsis
- 1 in 2 die
- More than 1 million cases of sepsis are reported per year
Procalcitonin, a 116 amino acid polypeptide prohormone of calcitonin has emerged as the most sensitive biomarker to aid diagnosis of bacterial sepsis. Synthesized primarily by the C-cells of the thyroid gland, and to a lesser extent in the neuroendocrine tissue of other organs such as the lungs and intestines, Procalcitonin is normally present in the blood at a very low level.
However, production can be stimulated by inflammatory cytokines and bacterial endotoxins, causing larger amounts of Procalcitonin to be released in response to infection, particularly systemic bacterial infections.

Procalcitonin Levels and Sepsis Risk:
| Severity of Sepsis | PCT concentration in the blood |
|---|---|
| Healthy | 0-0.05 ng/ml |
| Low Sepsis Risk | 0.05-0.5 ng/ml |
| Sepsis Risk | 0.5-2 ng/ml |
| High Sepsis Risk | > 2 ng/ml |
Interpretations of Procalcitonin results:
LOW LEVELS
- Low risk of sepsis
- Localized infection
- A systemic infection that is less than six hours old
- Transplant rejection
- A viral infection or trauma – post-surgery or otherwise
HIGH LEVELS
- High probability of sepsis, i.e., a bacterial cause for the symptoms
- Higher risk of progression to severe sepsis and then to septic shock
DECLINING LEVELS
- Response to therapy
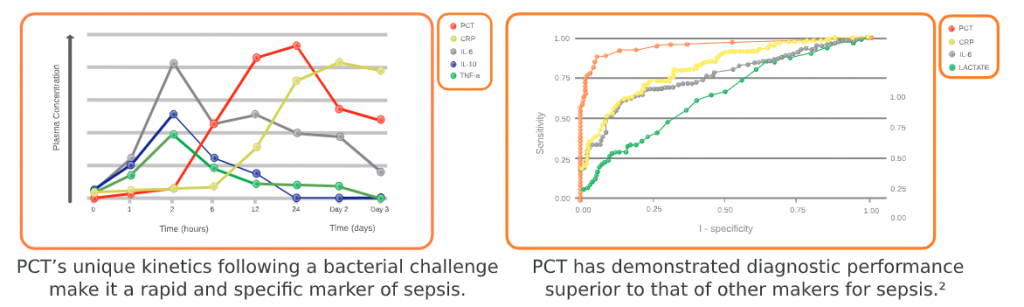
Why Procalcitonin is a better biomarker for Sepsis?
Compared to C-reactive protein (CRP), IL 4, IL6, Lactate – other biomarkers frequently used to aid diagnosis of sepsis – Procalcitonin shows better correlation, sensitivity and specificity in the event of bacterial infection. This favourable kinetics potentially enables earlier diagnosis of sepsis and better monitoring of its progression.
Interpretation of Results:

Ordering Information:
| Product | Specimen | Shelf life | Pack size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Procalcitonin (PCT) Rapid Card Test | Whole Blood/ Serum/ Plasma | 24 months | 5 Tests |
